Triassic Period: The structure of the animal world in Triassic Era
Preview

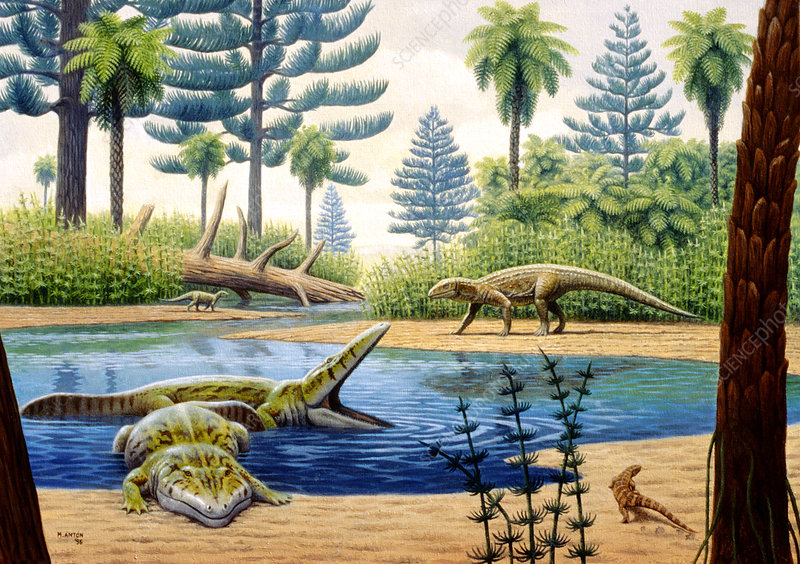
Seed ferns like Glossopteris and early species of gymnosperms (seed plants, such as the evergreens, in which the seeds are not enclosed) dominated the early Triassic terrain. Cycads, cycadeoids (like Pterophyllum, Zamites, and Williamsonia) and bennettitaleans, with tufts of tough, palm-like leaves and a woody trunk, were abundant in the Triassic. Also around were liverworts, mosses, smaller horsetails, club mosses, ferns, tree ferns (like Psaronius and glossopterids), ginkgophytes (like Baierophyllites), Filincophytes (like Macrotaeniopteris), Araucaria (the monkey puzzle tree), Bjuvia, Filincophytes (like Clathopteris), Lycopsids (like Sigillaria) and yews. "Cheiroleps" (conifers from the group Cheirolepidiaceae) dominated the northern latitudes during the Triassic period.
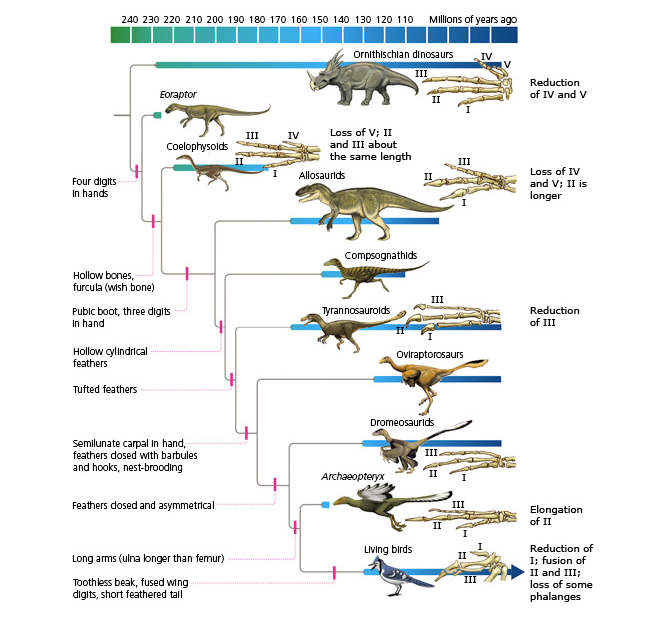
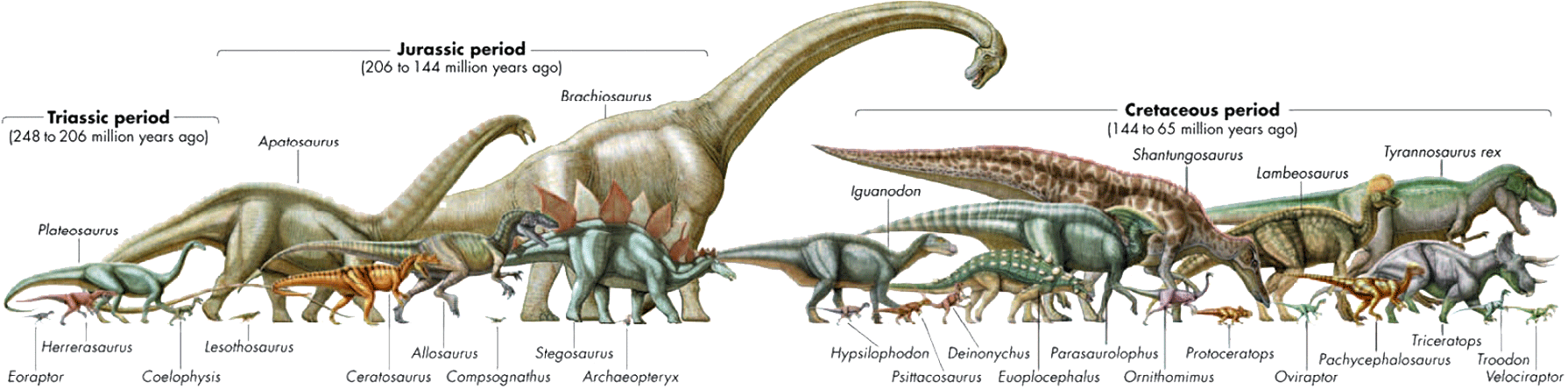
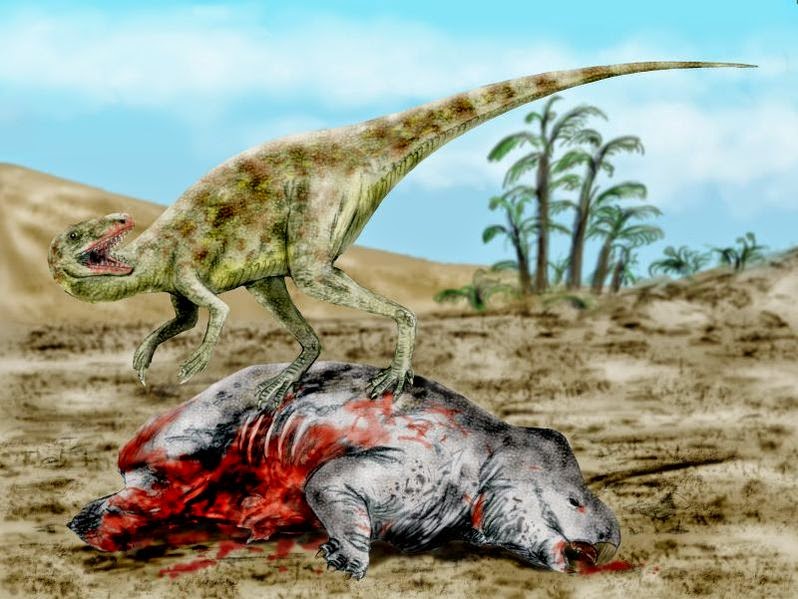
Relatively small dinosaurs evolved during the mid Triassic period. The early plant-eating dinosaurs included Fabrosaurids (like Lesothosaurus), Heterodontosaurids (like Heterodontosaurus) and prosauropods (like Plateosaurus). They were fast-moving plant-eaters that probably ate low-lying plants. Many, like Plateosaurus, may have been able to rear up on two legs to reach taller vegetation.
During the first half of the Triassic, however, dinosaurs were still a long way from ruling the Earth. They had a variety of competitors, including close relatives from the same animal group that dinosaurs themselves belonged to, the archosaurs ("ruling reptiles"). Crocodile-like terrestrial predators were among the most successful of these archosaur rivals but they had died out by the end of the Triassic. Dinosaurs were the big success story of the Triassic but another group of animals was beginning to emerge, too. These were the cynodonts, small, mammal-like creatures that lived in burrows. They probably laid eggs may have been warm blooded. An extinction event just before the Triassic began had given dinosaurs a leg-up on to the evolutionary ladder. As the period came to a close, another extinction event occurred. Geologists don't know what caused it but, once again, large numbers of sea and land animals were wiped out - although the effects are not believed to have been as severe as the extinction event just before the Triassic Period opened. In any event, dinosaurs came through the crisis stronger than ever, setting the stage for an explosion in numbers and diversity.